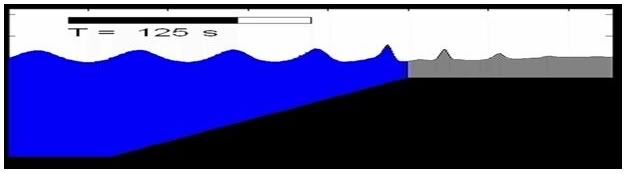
Another case has been carried out in order to simulate propagation of non-breaking regular wave on a sloping beach. Wave shoaling is analyzed and the result of computation is compared with analytical solution. Given wave properties condition are exactly the same with the previous computation at the left boundary. At the right boundary, the shallow water depth is located at the breaking location and was calculated from Goda formula.
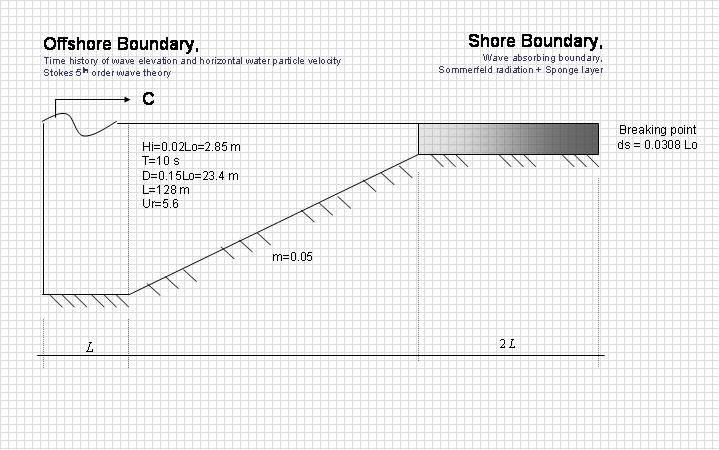
In this simulation wave transformation increasing in their wave heights during propagate to shore are well simulated. With further decrease in water depth an asymmetrical wave profile are also clearly observed.
If waves are incident normal to a beach with straight and parallel bottom contours, change in the wave profile is caused solely by change in water depth as so-called wave shoaling. Under this condition, wave shoaling over a sloping bottom can be observed to occur as follows: The waves first decrease and then gradually increase in height, maintaining symmetrical front and rare faces. With further decrease in water depth, the wave height increases rapidly to produce an asymmetrical wave profile; finally waves break.
In perturbation methods, the effect of the bottom slope is treated as a small perturbation within the framework of theories for a horizontal bottom. For a mildly sloping bottom, Kakutani (1971) extended the K-dV equation, which governs the transformation of first-order cnoidal waves traveling in uniform depth. Shuto (1974) treated wave height change based on Kakutani’s equation. The result in an approximate form is expressed as follows:
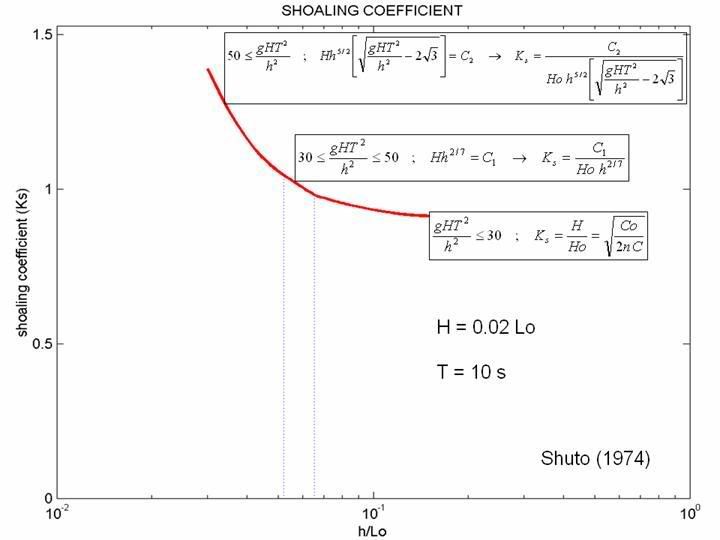
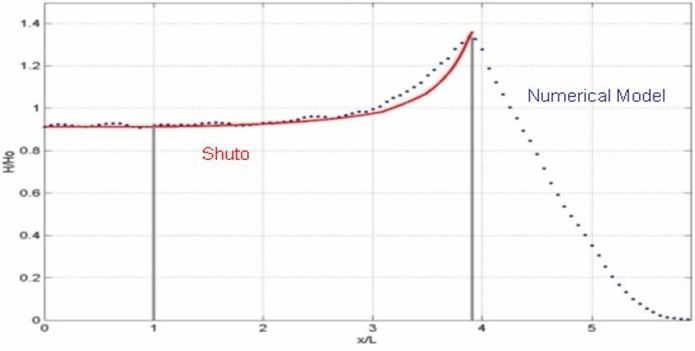
Comparison between analytical (Shuto, 1974) and numerical solution shows good agreement. The analytic solution is indicated by a red line while the numerical solution is indicated by a blue dotted-line. It may also conclude from figure below that Sommerfeld radiation and sponge layer are well effective in order to absorb long and short wave respectively.
Simulation of Non-breaking Regular Wave Propagation on a Constant Depth
Simulation of Breaking Regular Wave Propagation on a Sloping Beach up to Very Shallow Water Depth
Simulation of Non-breaking Regular Wave Runup Propagation on a Sloping Beach
Simulation of Breaking Regular Wave Runup Propagation on a Sloping Beach